Vocabulary & reading are interdependent.
The Importance of Teaching Morphology
- 4th-grade students with a strong understanding of morphology have higher reading comprehension scores (Kieffer & Lesaux, 2007).
- By 5th grade, students' understanding of morphology is a better predictor of reading comprehension than their vocabulary level (Kieffer & Lesaux, 2007).
Ways To Make New Words in English
Tips for Teaching Vocabulary
-
Teach compound words.
Demonstrate how two words can be combined together to form new words. Discuss the meaning of each word and the new meaning when they are combined.
-
Teach homonyms.
Many words carry more than one meaning. For example, to fix can mean to repair. It can also mean to attach.
-
Teach the meaning of prefixes.
For example, pre- as in prefix means before. Prefixes are letters attached before the base.
-
Teach the meaning of suffixes.
Suffixes often carry grammatical meaning. Adding an -s to a noun turns it from singular to plural.
-
Teach accurate suffixing rules.
Logic of English uses a flow chart with three spelling rules to accurately add a suffix to any word.
-
Teach common Latin & Greek roots.
Multisyllabic words are often based on Latin and Greek roots. Knowing the meaning of a root can unlock hundreds of new words.
-
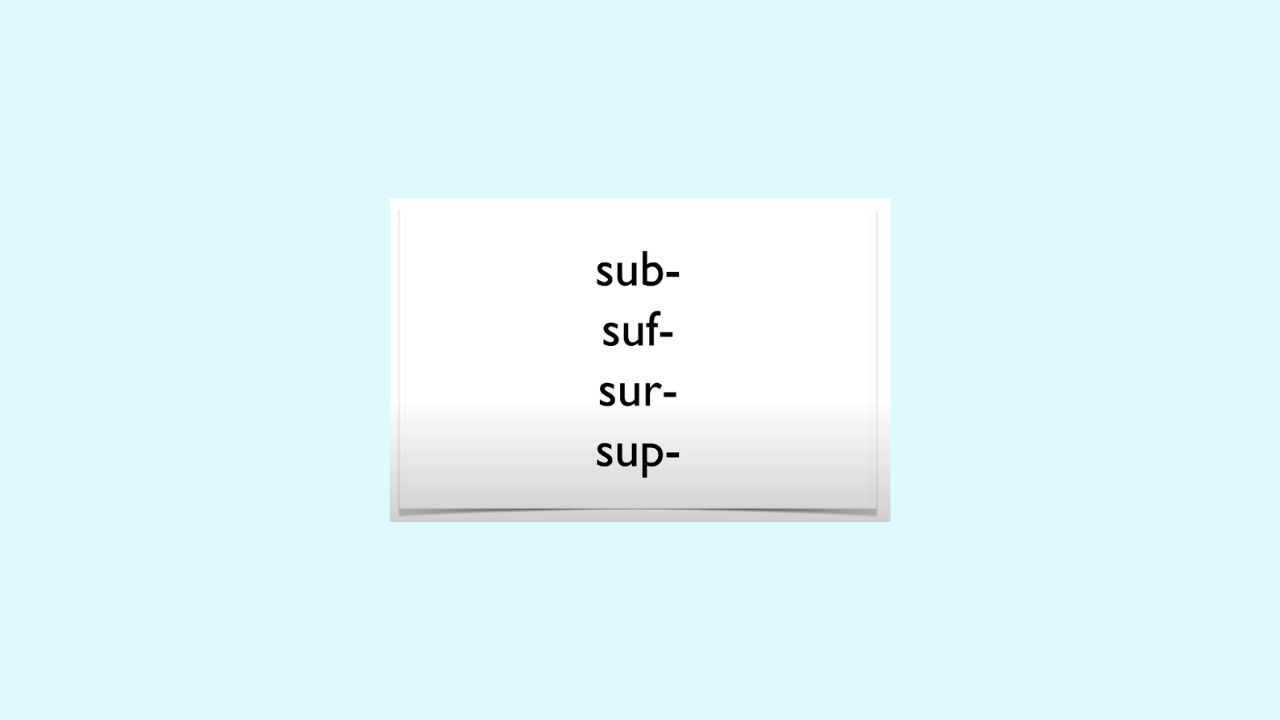
Teach Latin prefixes.
Latin prefixes also carry meaning. Latin prefixes can change their spelling based on the sound after the prefix.
-
Demonstrate connections between words.
Striving readers struggle to recognize the meaning of words that include a change to the sounds (Richards et al., 2006; Kieffer & Lesaux, 2007). Explicit vocabulary instruction can help them to understand the relationship between words.
Bring Morphemes to Life with Make It Make Sense: Morphology
Make It Make Sense: Morphology not only introduces students to morphology concepts like prefixes, suffixes, and roots, but it also serves as a visual guide to over 50 of the most common English morphemes. It empowers students to access the knowledge they need to quickly grow their own vocabulary! Learn more about how to use this resource and download free, corresponding activities on our blog!
The sounds, spellings, and meaning of written words are intertwined.
-
WR
-
wrench
-
wrinkle
-
wring
-
wrap
-
wrist
How Morphology & Phonics Work Together
Word Reading Strategy
Decode First, Then Discover!
If it makes sense, keep reading! But if at anytime a word doesn't make sense, pause and use these strategies to discover the word!
Morphology
2019 Teacher Training
References
Kieffer, M. J., & Lesaux, N. K. (2007). Breaking Down Words to Build Meaning: Morphology, Vocabulary, and Reading Comprehension in the Urban Classroom. The Reading Teacher, 61(2), 134–144. https://doi.org/10.1598/rt.61.2.3
Richards, T. L., Aylward, E. H., Berninger, V. W., Field, K. M., Grimme, A. C., Richards, A. L., & Nagy, W. (2006). Individual fMRI activation in orthographic mapping and morpheme mapping after orthographic or morphological spelling treatment in child dyslexics. Journal of Neurolinguistics, 19(1), 56–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroling.2005.07.003









































